SU-8
SU-8 is a negative, epoxy based, near-UV photoresist designed for MEMS and other microelectronic applications. It was originally developed and patented by IBM. SU-8 is processed using standard lithography techniques. When SU-8 is exposed to UV light its molecular chains cross-link, causing the SU-8 to solidify. SU-8 is highly transparent in the ultraviolet range. This allows for the fabrication of relatively thick (hundreds of micrometers) structures with nearly vertical side walls. Two companies have licenses from IBM to sell SU-8: MicroChem and Gersteltec.
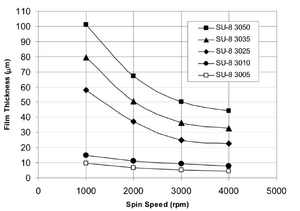
In the Cleanroom of the University of Copnehagen we provide SU-8 3050.
Recommended developer: mr-Dev 600
Technical datasheets
Fabrication recipe
Dehydration
- Place your wafer on a hotplate for t=10 minutes at T=185˚C.
- Let the wafer cool down.
Spin coat
- Dispense 1 ml of resist for each inch (25 mm) of substrate diameter (4ml for a 4 inch wafer)
- Spin at 500 rpm for 5-10 sec with acceleration of 100 rpm/second
- Spin at 3000 rpm for 30 sec with acceleration of 300 rpm/second
- Soft bake at 95C for 15 mins
Expose pattern with upg501 Heidelberg
Post bake exposure
- 95C for 5 mins
- Post bake exposure should take place directly after exposure
Development
- Develop for 10 minutes in developer mr-Dev 600
- Rinse for 30 seconds in Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA)
- Dry with N2 gun